The NIS2 Directive was adopted in 2022 and officially came into force in January 2023, imposing new and stricter cybersecurity and risk management obligations on public and private entities that manage essential services. Although the deadline for EU member states to transpose it into national legislation was October 2024, many organizations in 2025 still face critical questions: How does NIS2 compliance affect the use of artificial intelligence? What risks are involved? What measures must be implemented?
This article addresses those questions and offers practical solutions, including how tools like Nymiz can help organizations comply with the regulation without sacrificing innovation.
What is NIS2 compliance and why does it affect organizations using AI?
Understanding what NIS2 compliance details is essential for organizations seeking to adopt new technologies while maintaining their legal and cybersecurity responsibilities. The directive is not only about network protection—it’s a comprehensive regulatory framework that intersects with digital transformation strategies, including artificial intelligence.
Purpose of the directive
The NIS2 Directive (Network and Information Security Directive 2) is the EU’s main regulation to ensure the cybersecurity of essential services. It establishes broader and stricter requirements than its predecessor (NIS1) to enhance digital resilience in strategic sectors.
Who it applies to and why it includes AI
Although NIS2 does not explicitly mention artificial intelligence, it establishes general obligations that apply to any technology involved in the processing of critical information. This includes platforms, algorithms, or AI tools that access, process, or analyze sensitive or strategic data.
What does NIS2 require regarding AI usage?
As artificial intelligence becomes more embedded in organizational workflows, ensuring it aligns with regulatory expectations becomes crucial. While NIS2 does not provide a detailed protocol for AI, it imposes broad responsibilities that apply to any technology handling critical data—including AI-driven systems. Organizations must understand that compliance extends beyond infrastructure protection and includes how automated tools interact with sensitive data, how decisions are made, and how risks are managed across the entire digital ecosystem.
The regulation requires organizations to assess and mitigate technological risks, document processes, implement robust cybersecurity measures, and ensure operational continuity even in case of incidents.

Specific measures for systems using AI
When systems use AI, organizations must ensure:
- Controlled access to data used by algorithms.
- Human oversight of automated processes.
- Continuous risk evaluation.
- Security by design and by default.
- Transparency and traceability in automated decision-making
How to manage incidents involving AI under NIS2
NIS2 sets strict deadlines for reporting relevant incidents:
- Early warning: within the first 24 hours of detection.
- Full report: within a maximum of 72 hours.
- Final report: within one month after the incident.
This means that any breach, failure, or misuse of an AI system compromising the availability, integrity, or confidentiality of information must be treated as a critical incident.
Who is responsible for NIS2 compliance in AI environments?
Organizations using AI systems must establish robust internal governance and control frameworks to ensure NIS2 compliance. This goes beyond mere technical implementation: it includes defining clear lines of accountability, regularly training staff involved in AI workflows, conducting thorough impact assessments, and setting up detailed documentation processes.
These measures are critical not only to prevent incidents but also to provide evidence of compliance during audits. Moreover, governance models must be adaptable to the evolving nature of AI technologies, ensuring that new risks are quickly identified and managed.
Supply chain and third-party providers
Compliance is not limited to in-house systems. Under NIS2, organizations are explicitly required to assess and secure their digital supply chains, especially when third-party AI tools or cloud services are involved. This includes verifying that vendors adhere to equivalent cybersecurity standards, establishing contractual obligations for incident response collaboration, and performing periodic audits of provider performance.
Organizations must also ensure that any data shared with these external systems is protected via encryption, anonymization, or other privacy-preserving mechanisms. Failure to manage third-party risks effectively can result in regulatory penalties and reputational damage, especially in high-impact sectors like healthcare, finance, and public administration.
How to demonstrate NIS2 compliance when working with AI
Compliance must be demonstrable to national authorities. This requires:
Documented evidence of implemented technical measures.
Logs of activity, access, and data processing.
Regular risk assessments.
Mechanisms for traceability and active oversight of AI systems.
Risks and benefits of using AI under NIS2 compliance
Using AI in regulated environments can present both strategic opportunities and potential risks. In the context of NIS2 compliance, organizations must be particularly cautious when deploying AI models, as poor implementation may lead to data breaches, unexplainable decisions, or exploitable vulnerabilities.
On the other hand, well-managed AI supported by strong governance and security can accelerate processes, reduce human error, and improve threat response.
Potential dangers
A recent case illustrating the consequences of non-compliance was the cyberattack on El Corte Inglés in March 2025. The breach originated through an external provider, allowing attackers to access customer identification and contact data.
Although no official NIS2 violation was confirmed, the incident highlighted the urgent need to protect digital supply chains and apply strong cybersecurity measures—especially in complex ecosystems integrating AI. Under current regulations, such breaches can lead to fines of up to €10 million or 2% of global annual turnover, as stated by NIS2.
- Exposure of sensitive data if not properly protected.
- Biased or non-auditable automated decisions.
- Lack of control in self-evolving algorithms.
Opportunities and advantages
- Automating critical processes with integrated cybersecurity.
- Improving operational efficiency without sacrificing compliance.
- Reducing human errors in repetitive and sensitive tasks.
Practical solutions to ensure NIS2 compliance in AI projects
Faced with the challenge of complying with NIS2 requirements, organizations need practical strategies that not only ensure regulatory control but also enable the effective integration of technologies like artificial intelligence.
Implementing specific technical solutions and adopting a privacy-by-design approach is essential to ensure that automated systems do not compromise the integrity or security of data. Below are the key actions to balance technological innovation with regulatory compliance.
Recommended approaches
- Clear governance of AI systems.
- Privacy and security impact assessments.
- Integration of data anonymization from the design stage.
Benefits of anonymizing data
Anonymization irreversibly transforms personal data, meaning they are no longer subject to many legal obligations associated with identifiable data. This technique not only reduces the legal and technical sensitivity of data but also eliminates the risk of re-identification, providing an additional safeguard against security breaches.
In contexts where AI systems need access to large datasets to train models or make automated decisions, anonymization is an essential safeguard.
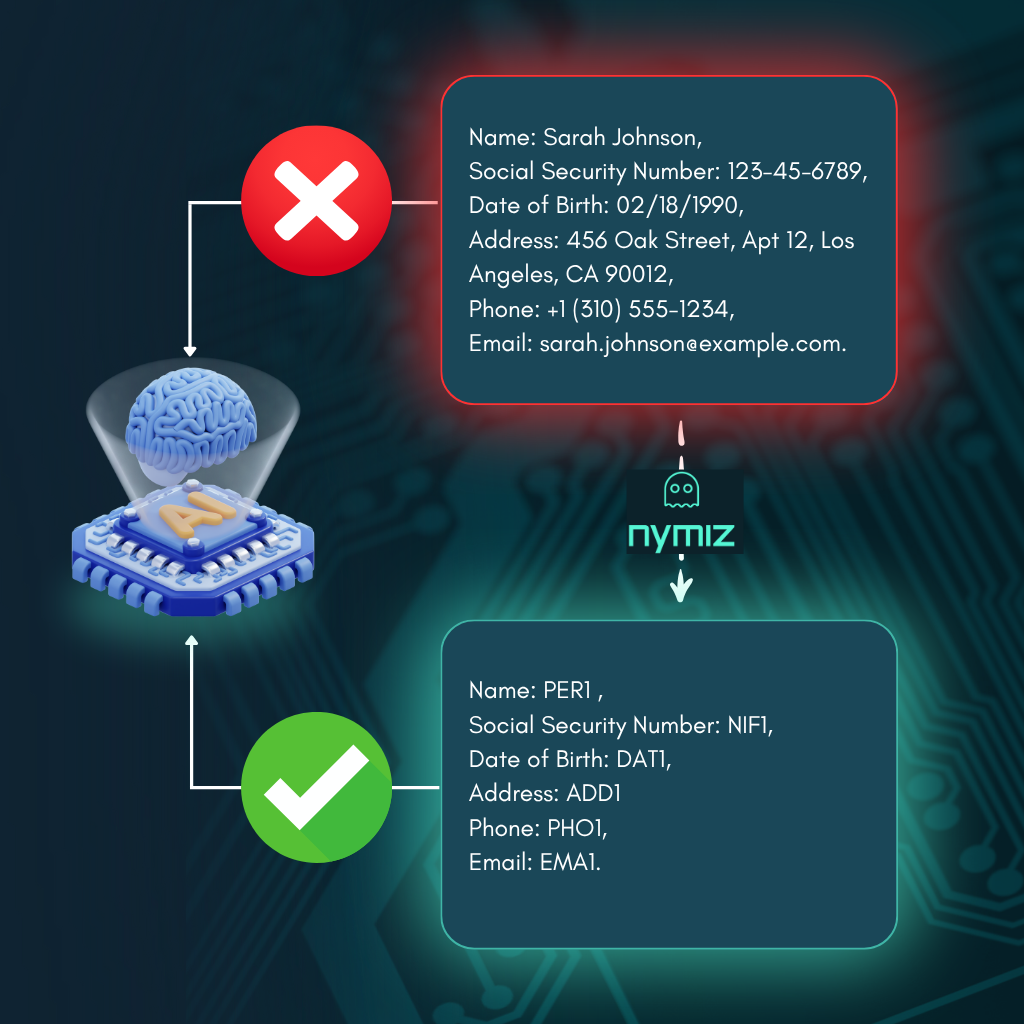
It allows systems to operate with realistic information without exposing personal data while complying with the minimization and privacy-by-design principles required by NIS2 compliance. Additionally, because it does not rely on encryption keys, anonymization avoids added risks linked to access management, offering a more robust and autonomous solution for highly regulated environments.
How Nymiz ensures NIS2 compliance when using AI
Nymiz provides an intelligent anonymization platform that adapts the type of anonymization to the data context, usage purpose, and associated risk level. This enables ethical, legal, and secure AI usage without compromising analytical quality.
Key functionalities:
- Automated anonymization of documents and free text.
- Anonymization in databases.
- Batch processing.
- Manual supervision and contextual adjustments.
- Traceability logs to comply with audits.
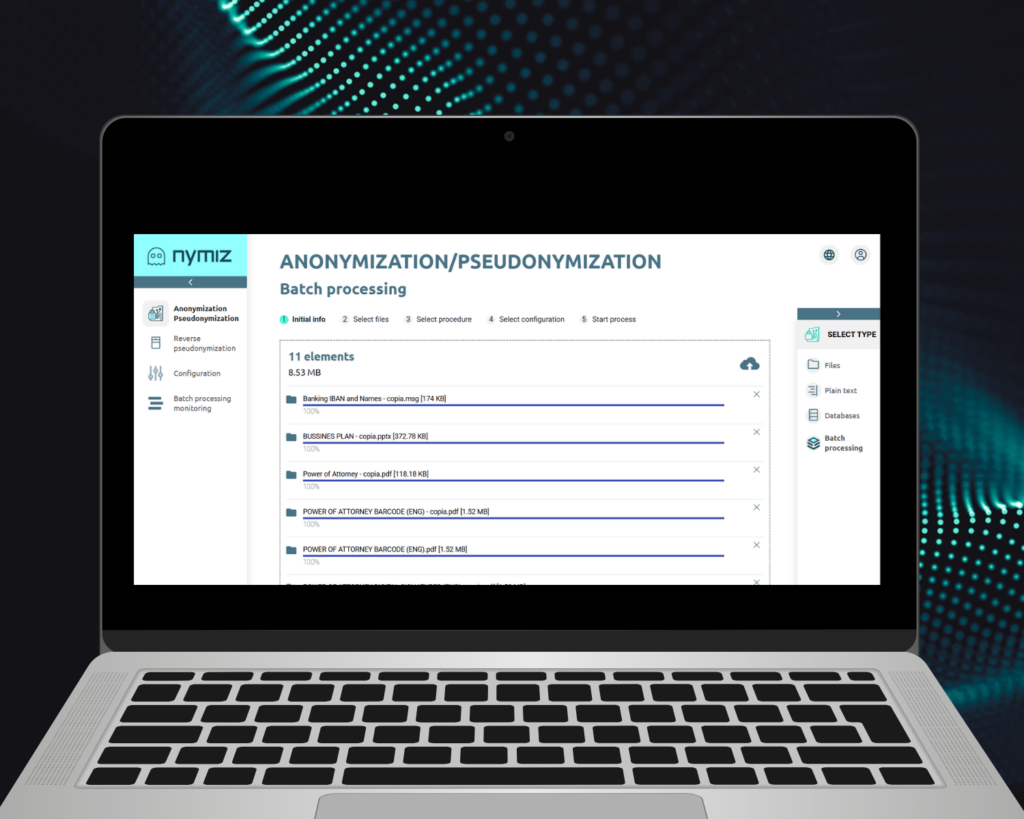
Integration with AI workflows and regulatory protection
Nymiz securely connects with AI-driven systems, ensuring that processed data is protected from the source through contextual anonymization. This integration supports privacy-by-design even in complex automated processes.
For example, in the healthcare sector, one of our clients implemented Nymiz to anonymize clinical reports before feeding them into a diagnostic AI system. The solution preserved the structure and semantics of the medical data without compromising patient privacy or violating NIS2 compliance. It also reduced manual review time by 80%, enhancing workflow efficiency while safeguarding personal data.
Thanks to its ability to scale securely and audibly, Nymiz empowers organizations to harness the full potential of artificial intelligence without undermining the core principles of European cybersecurity and data protection regulations.
Conclusion
NIS2 compliance is not incompatible with innovation. Integrating AI into organizational processes is feasible when proper measures are applied from the design stage, traceability is maintained, and privacy is guaranteed. Nymiz stands as a key ally in this effort—protecting data without blocking the value that artificial intelligence brings.






