The entry into force of the European Union’s AI Regulation (AI Act) marks a turning point for all organizations that use or develop AI-based systems. This regulatory framework, a global pioneer, establishes demanding requirements that, at first glance, may be perceived as an obstacle. However, with the right approach and the necessary tools, these challenges can be transformed into real competitive advantages.
What does the AI Regulation require?
The AI Regulation introduces a regulatory framework structured according to the level of risk posed by different artificial intelligence systems. For systems classified as high risk, the requirements are especially stringent and require a proactive approach from organizations. The main criteria and obligations that must be met are detailed below.

Risk classification and requirements in AI Regulation
The AI Regulation establishes a risk classification (unacceptable, high, limited, and minimal) and, depending on the level of risk, imposes specific requirements:
- Unacceptable risks: These systems are prohibited as they pose a clear threat to fundamental rights. Examples include social scoring by governments or the use of AI to manipulate behavior through subliminal techniques.
- High risks: These require strict compliance controls. These apply to sectors such as justice, human resources, healthcare, banking, and critical infrastructure. These must meet the following requirements:
- Identification of the AI systems used.
- Risk assessment and mitigation measures.
- Technical documentation and recordkeeping.
- Ensure transparency and traceability.
- Effective human oversight.
- Compliance with cybersecurity and privacy requirements.
- Limited risks: These must comply with minimum obligations, such as informing the user that they are interacting with an AI system (e.g., a chatbot).
- Minimal risks: These represent the vast majority of applications and are not subject to additional requirements under the regulation.
Challenges facing organizations
The implementation of the AI Regulation presents multiple operational, technical, and organizational obstacles for entities developing or adopting AI-based solutions. These challenges not only affect legal compliance but also efficiency, traceability, and corporate reputation.
One of the most representative examples of non-compliance with the principles of the AI Act and the GDPR is the case of Clearview AI. This company was fined €30.5 million by the Dutch Data Protection Authority for using facial recognition technologies without consent, violating fundamental principles such as transparency, data minimization, and the legal basis for processing.
This case highlights that even advanced technologies can become dangerous without proper privacy and ethics management, a view shared by the European Data Protection Board (EDPB), which considers that a service like the one offered by Clearview AI is not compliant with the EU data protection regime. In sectors such as legal and financial services, where AI systems have direct implications for people’s rights, oversight and compliance become even more critical.
Furthermore, compliance with the requirements of the AI Regulation is not limited to formalities: it involves addressing a series of complex operational requirements, ranging from transparency to technical documentation. The following requirements, while essential to ensuring the ethical and legal use of AI, pose a considerable challenge for many organizations, especially when they must scale across multiple departments or technological solutions:
- Complexity in identifying and classifying AI systems. Many companies lack a clear map of where and how AI is applied in their processes. This lack of visibility makes regulatory compliance difficult and can expose them to sanctions.
- Third-party auditing and oversight. When third-party solutions are integrated or APIs are used with AI components, the organization remains responsible. This requires auditing suppliers and requiring evidence of compliance.
- System transparency and explainability. Complex AI models can operate as a “black box.” Explaining how decisions are made in a way that is understandable to users and auditors is key and often difficult.
- Ensure the privacy of personal data. AI requires data to train and operate. Without adequate data protection, compliance with the GDPR and the AI Act is compromised.
- Generation and maintenance of technical documentation. Compliance is not enough: it must be demonstrated with reports, records, and traceability of decisions. This administrative burden can be overwhelming if done manually.

Turning compliance into a competitive advantage
Compliance with the AI Regulation should not be seen solely as a legal burden. In fact, it can become a powerful strategic tool to position organizations as leaders in digital ethics, privacy, and technological governance.
How to transform obligation into leadership
Compliance with regulations is not just about avoiding fines: it is also about demonstrating technological maturity, commitment to fundamental rights, and ethical leadership.
- Increases customer and market trust: Organizations that demonstrate they manage AI responsibly gain credibility. This is especially important in sectors such as legal, healthcare, financial, and public services.
- Improves product and service quality: Traceability and control improve efficiency and allow for identifying improvements in automated processes.
- Promotes innovation on a solid foundation: Having a clear regulatory foundation allows for innovation with greater security and lower risk.
- Positions the organization for future regulations: Proactive compliance with the AI Regulation facilitates adaptation to new national and international regulations.
Privacy as a catalyst for AI Regulatory compliance
In a landscape of rapidly growing regulatory demands and intensifying oversight of the use of technologies such as AI, ensuring the privacy of our assets is no longer optional but essential. To achieve this, it is essential to rely on solutions that integrate privacy by design and offer verifiable technical mechanisms.
Nymiz is presented as a robust solution to facilitate regulatory compliance without compromising data value or hindering AI-driven innovation. Below, we explore how we achieve this.
Key benefits of Nymiz for privacy protection
Nymiz is the tool that transforms regulatory challenges into strategic opportunities. Our solution allows for:
- Automatically anonymizing large volumes of data: protecting privacy without losing analytical value in just a few minutes.
- Providing traceability and control: generating documentary evidence to audit systems and processes.
- Ensure compliance with GDPR and the AI Act: from documentation to risk assessment.
- Collaborate with your legal and technical teams: Facilitating a cross-functional, secure, and accurate implementation.
- Document anonymization (structured and unstructured): Directly addresses the challenge of ensuring the privacy of personal data in reports or files processed by AI systems. This functionality enables compliance with the AI Regulation’s requirement to protect sensitive data without compromising its usefulness.
- Plain text anonymization: Essential for technical documentation processes, allowing records to be maintained that are accessible but free of personally identifiable information.
- Manual oversight: Addresses the need for effective human oversight, allowing anonymization processes to be reviewed and validated, and adjusted if necessary.
- Batch processing: Automates mass document anonymization, streamlines workflows, and allows for oversight of the entire process from a single location
- Database anonymization: Allows for the implementation of risk mitigation measures by anonymizing records directly at the source, ensuring traceability and compliance from the outset.
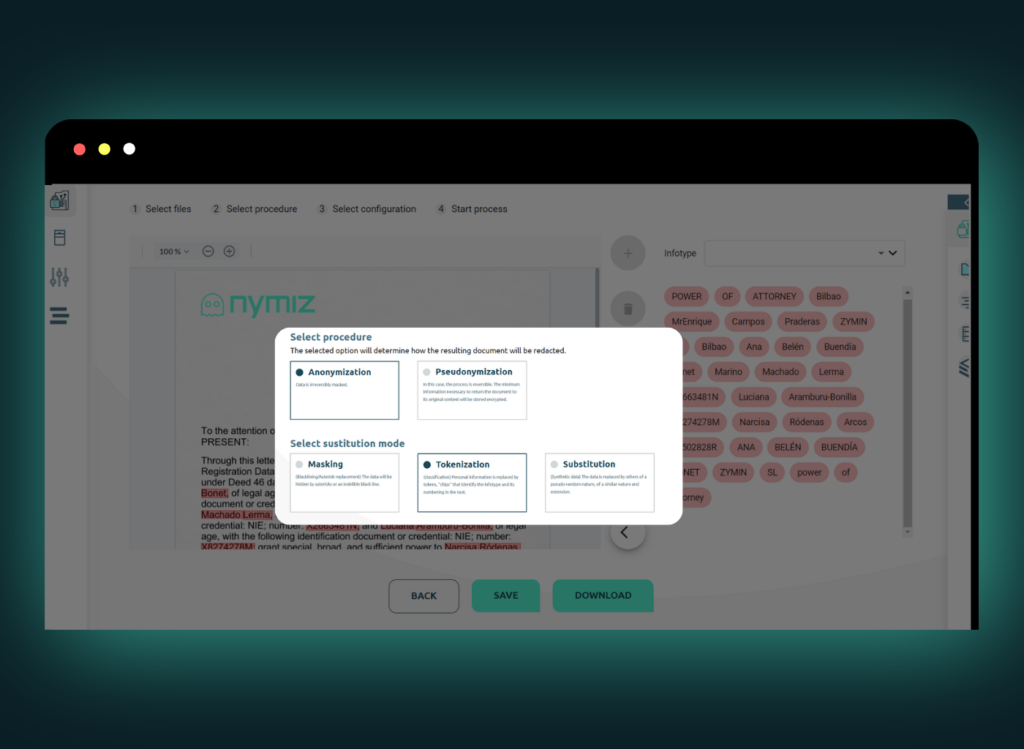
With this approach, Nymiz aims to ensure that organizations and professionals can share information with AI systems without sacrificing privacy, context, or analytical value. This capability not only guarantees the confidentiality of personal data but also enables the application of artificial intelligence securely and responsibly.
Thanks to its integration into workflows, Nymiz acts as a layer of protection and traceability throughout the entire data lifecycle. This enables regulatory-compliant automation, allowing companies to innovate without fear of non-compliance, sanctions, or reputational risks. Ultimately, it makes compliance a strategic enabler for an ethical and sustainable digital transformation.
Conclusion
The AI Regulation places significant demands on the company, but it also offers a unique opportunity to differentiate itself through responsible compliance. Throughout this article, we’ve analyzed how this regulation affects organizations, the challenges it poses, and how solutions like Nymiz can address them without compromising privacy or the ability to innovate.
Complying with the AI Regulation not only avoids sanctions: It’s a strategy to position yourself as an ethical and trusted leader in the use of advanced technologies.
Explore how our solutions can help you comply and excel. Book a personalized demo and discover how to transform compliance into a competitive advantage.






