In recent years, the number of redacted documents, particularly in PDF format, has grown exponentially due to the rise of automated processes powered by artificial intelligence. AI-generated reports, automated legal analyses, and digital workflows have led to the circulation of thousands of documents containing sensitive data across organizations every month. However, this growing volume has revealed a critical issue: many of these documents are not properly secured.
A high-profile example is the Jeffrey Epstein case. Over the course of multiple judicial publications, thousands of supposedly redacted pages were released. However, the names of individuals involved were still visible through basic copy/paste functions or OCR tools. The failure wasn’t technical, it was the lack of automated processes, technical validation, and proper tools to ensure irreversible redaction.
This is not an isolated incident. According to global data breach reports, 11% of breaches are linked to errors in document handling, including poorly executed redactions. In a world where PDFs remain the most common format for sharing contracts, reports, rulings, or medical records, the risk increases with every click of “send.”
This article explains why manual processes to redact PDF documents are no longer viable in 2026. We’ll outline the most common errors, hidden risks within metadata and invisible layers, how to automate security from the ground up, and why tools like Nymiz are essential for robust data governance in the era of AI.
What Is Document Redaction and Why Does It Matter?
Beyond compliance, redacting a PDF document properly means preventing it from becoming an invisible risk in an organization’s data management strategy. In the past year alone, over 18 billion PDF documents were edited with Adobe Acrobat using black boxes as a redaction method.
However, this visual-only approach fails to ensure true data security: many of these documents still contain personal, financial, or clinical data that (if not fully removed across all file layers) can be recovered and leaked, resulting in data breaches, regulatory penalties, and serious reputational damage.
Redaction ≠ Concealment: What Does Secure Redaction Really Mean?
To securely redact PDF documents means data destruction, not concealment. Technically, this involves:
- Removing underlying text
- Deleting invisible layers
- Scrubbing embedded metadata
- Ensuring no visual overlays or cropping can be reversed
Anything else (such as drawing black boxes or overwriting text) is cosmetic, not secure.
Why It’s a Critical Practice in 2026
Global Regulatory Compliance
The world’s most stringent regulations (GDPR, HIPAA, LGPD, PDPB, CCPA) require irreversible data removal. In 2025, combined fines for redaction failures in the US and EU exceeded $270 million.
Reidentification Risks
Even if names are concealed, documents that retain dates, codes, or indirect identifiers can be cross-referenced to reidentify individuals.

The Most Common Mistakes When You Redact PDF Documents (And How to Avoid Them)
At Nymiz, we highlight five structural failures that frequently occur in highly regulated sectors. Here’s what they are, their impact, and how to prevent them.
1. Visual Redaction Without Removing Underlying Text
What Happens
One of the most common redaction errors is using graphic editing tools (black boxes, color blocks, or visual cropping) to cover visible text without deleting the underlying content. While the data may seem hidden, the original text remains accessible through copy/paste, search, or OCR tools.
This was one of the critical failures in the Epstein case, where sensitive names and details appeared in supposedly redacted files. The visible layers masked the content but did not remove it.
How to Avoid It
- Use software that edits the PDF structure and permanently deletes sensitive content.
- Perform post-redaction validation with forensic analysis tools or OCR simulators.

2. Missing OCR on Scanned Documents
What Happens
Many documents are image-based, either scanned or captured. Without applying Optical Character Recognition (OCR), redaction tools cannot detect the content, leaving sensitive data intact and invisible to the system.
How to Avoid It
- Integrate an OCR step into your document processing pipeline.
- Ensure the OCR solution is multilingual and can process low-quality scans.
3. Publishing Without Human Oversight
What Happens
Even when redaction tools are used, many organizations fail to verify their proper execution. This includes ignoring invisible data layers, annotations, prior versions, or embedded comments. The Epstein case also showed that without final validation, a single error can become a global scandal.
How to Avoid It
- Include a final automated quality control step.
- Use tools with logging and audit trails for compliance evidence.
4. Neglecting Metadata and Document History
What Happens
PDF files often contain hidden information such as the author, edit dates, revision history, embedded links, or inserted comments. This metadata can undermine privacy even when the visible content is redacted.
How to Avoid It
- Use professional tools to scrub metadata.
- Always export a flat, final version of the document.
5. Sharing Without Anonymization or Access Control
What Happens
Even a perfectly redacted document can pose risks if shared without restrictions. Lack of anonymization, expiration, or access limits can lead to unauthorized reuse or exposure.
How to Avoid It
- Apply anonymization, encryption, or password protection.
- Use systems with traceable access logs and automatic expiration features.
How to Redact PDF Documents Securely in 2026: A Step-by-Step Guide
Effectively redacting a PDF document is not about guesswork or good intentions. It requires a methodical anonnymization process combining technical precision, control, validation, and auditability. Experts in privacy and information security recommend at least five key steps:
Step 1: Classify Sensitive Data
Before redacting, identify what needs to be removed: PII, PHI, financial, or confidential data. This classification should align with the applicable regulatory framework (GDPR, HIPAA, LGPD, etc.) and be context-specific.
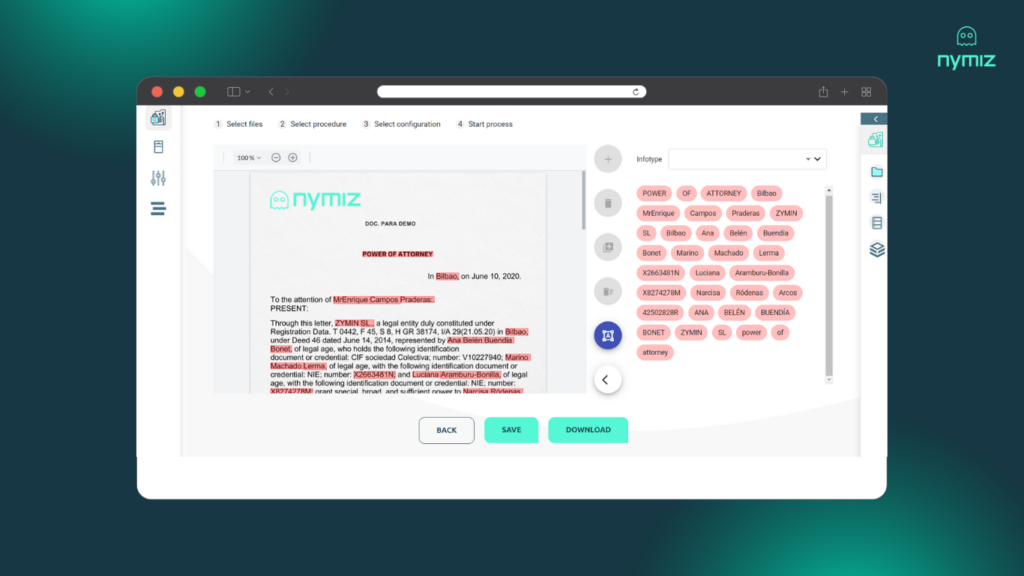
Step 2: Apply Advanced OCR
If your documents are scanned or image-based, apply Optical Character Recognition (OCR). Advanced solutions use AI to interpret distorted or multilingual text in low-quality documents.
Step 3: Run Automated Anonymizaton
This is where classified data is irreversibly removed. The tool should support custom rules to delete text, invisible layers, annotations, and cross-references. Automation ensures consistency and reduces human error.
Step 4: Scrub the Entire Document
Redaction doesn’t end with masking text. You must also delete previous versions, embedded metadata, document properties, and any digital trace that could reconstruct the content.
Step 5: Secure the Final Output
Finally, add extra safeguards: structural anonymization, encryption, passwords, access control, and expiration policies to prevent unauthorized circulation.

Automating PDF Redaction with Smart Tools
Organizations that automate document protection save up to $1.76 million per breach. In an era where AI is embedded in numerous workflows, from report generation to legal summaries or clinical analytics, thousands of documents are redacted and shared monthly, many with embedded sensitive data. Without proper controls, each document becomes a potential risk vector.
Why Automate?
- Volume and speed exceed human capacity
- Reduces human error
- Enables compliance through traceable logs and validations
Risks of Not Automating
- 68% of AI-related data breaches in 2025 stemmed from improperly anonymized data
- Only 23% of companies have document validation processes using AI
What do Anonymization Methods Offer?
- Over 95% accuracy in detecting sensitive data
- Integration with document workflows and AI pipelines
- Full traceability from origin to final file
Nymiz: Advanced Anonymization for Bulletproof Redaction
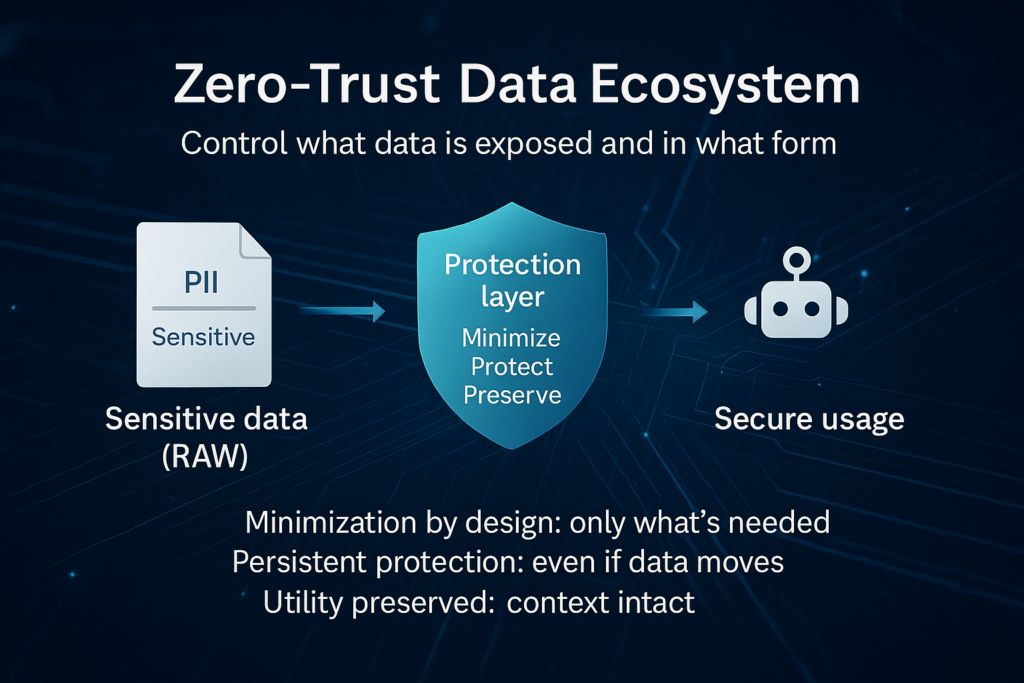
Nymiz turns PDF redaction into a strategic pillar of data protection and regulatory compliance. Its technology is based on AI-powered detection, analysis, and secure deletion of sensitive information in any document type. Unlike other tools, Nymiz operates across all file layers (text, OCR, metadata, history), ensuring irreversible, verifiable, and auditable redaction.
It features a unique contextual approach, allowing it to detect complex risk patterns, such as combinations of fields that may allow reidentification even after core data has been removed. This makes Nymiz essential for organizations handling large volumes of personal data with enhanced security needs.
What Makes Nymiz Different?
- Detects PII, PHI, and contextual sensitive data in multiple formats
- Includes multilingual OCR processing
- Eliminates invisible layers, metadata, and previous versions
- Generates secure, export-ready files
- Preserves analytical and semantic value in redacted documents
- Seamlessly integrates into AI, data governance, and compliance ecosystems
Real-World Use Cases
- Mass redaction of court rulings
- Protection of clinical records in research workflows
- Secure delivery of regulatory reports
- Public release of administrative resolutions under GDPR
The Epstein Case: A Failed Redaction That Exposed Structural Risks
In early 2024, over 900 pages of court documents from the Epstein case were released. While announced as securely redacted, technical audits revealed a cascade of failures:
- Underlying text still visible via OCR or copy/paste
- Files shared without version control or metadata cleanup
- No final validation before publication
These oversights led to names, positions, and associations being leaked across media and social networks. This case became global evidence that poor redaction isn’t just a technical error, it’s a strategic failure with legal, reputational, and social consequences.

Privacy and data protection experts agree: visual redaction alone, without data layer elimination, is not enough. Had automated secure redaction been applied—covering irreversible deletion, OCR validation, and version control—the risk would have been significantly reduced. At Nymiz, we know that the key lies in integrating purpose-built tools that operate across all document layers and adapt to the data’s context.
This real case illustrates why manual redaction or generic tools fall short. What failed in a high-profile court could just as easily happen in a company, hospital, or public institution; unless professional standards and dedicated technology are applied.
Conclusion
In 2026, privacy requires precision, not improvisation. To redact PDF documents properly means far more than blacking out names: it means applying technical, auditable measures to ensure irreversible destruction of sensitive data. The Epstein case wasn’t a fluke; it was a reflection of a deeper problem: a data culture that underestimates the risk hidden within documents.
Every document today can either become a breach or a barrier. Automating your PDF redaction, with tools that understand context and erase information reliably, is key to achieving compliance and safeguarding the operational value of data. With Nymiz, secure redaction becomes a cornerstone of modern data governance.
Want to see how automatic PDF document redaction works with Nymiz? Book a free demo and discover how we tailor it to your case, in just 15 minutes.






